If Else Ladder in Java Example
In programming, we use the if..else statement to run a block of code among more than one alternatives.
For example, assigning grades (A, B, C) based on the percentage obtained by a student.
- if the percentage is above 90, assign grade A
- if the percentage is above 75, assign grade B
- if the percentage is above 65, assign grade C
1. Java if (if-then) Statement
The syntax of an if-then statement is:
if (condition) { // statements } Here, condition is a boolean expression such as age >= 18.
- if condition evaluates to
true, statements are executed - if condition evaluates to
false, statements are skipped
Working of if Statement
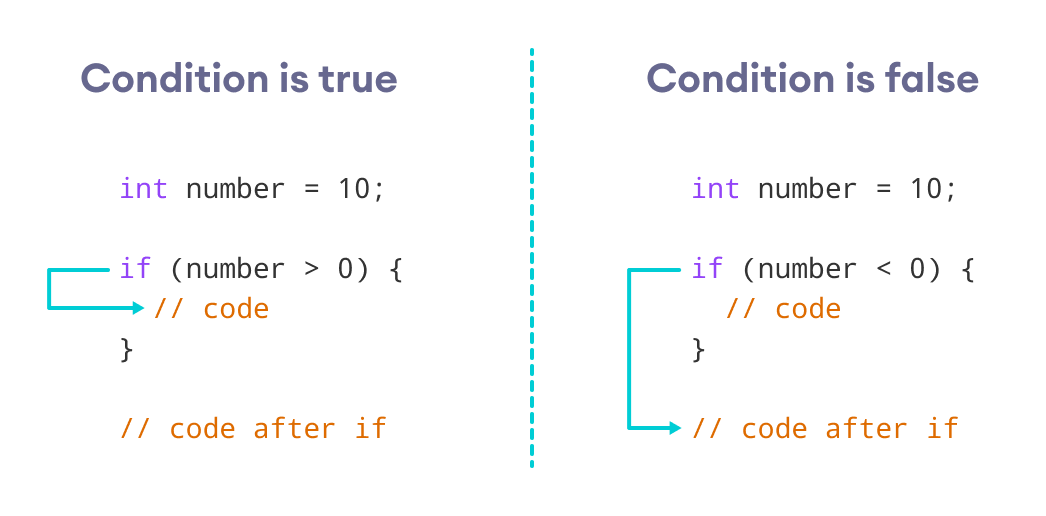
Example 1: Java if Statement
class IfStatement { public static void main(String[] args) { int number = 10; // checks if number is less than 0 if (number < 0) { System.out.println("The number is negative."); } System.out.println("Statement outside if block"); } } Output
Statement outside if block
In the program, number < 0 is false. Hence, the code inside the parenthesis is skipped.
Note: If you want to learn more about about test conditions, visit Java Relational Operators and Java Logical Operators.
We can also use Java Strings as the test condition.
Example 2: Java if with String
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // create a string variable String language = "Java"; // if statement if (language == "Java") { System.out.println("Best Programming Language"); } } } Output
Best Programming Language
In the above example, we are comparing two strings in the if block.
2. Java if...else (if-then-else) Statement
The if statement executes a certain section of code if the test expression is evaluated to true. However, if the test expression is evaluated to false, it does nothing.
In this case, we can use an optional else block. Statements inside the body of else block are executed if the test expression is evaluated to false. This is known as the if-...else statement in Java.
The syntax of the if...else statement is:
if (condition) { // codes in if block } else { // codes in else block } Here, the program will do one task (codes inside if block) if the condition is true and another task (codes inside else block) if the condition is false.
How the if...else statement works?
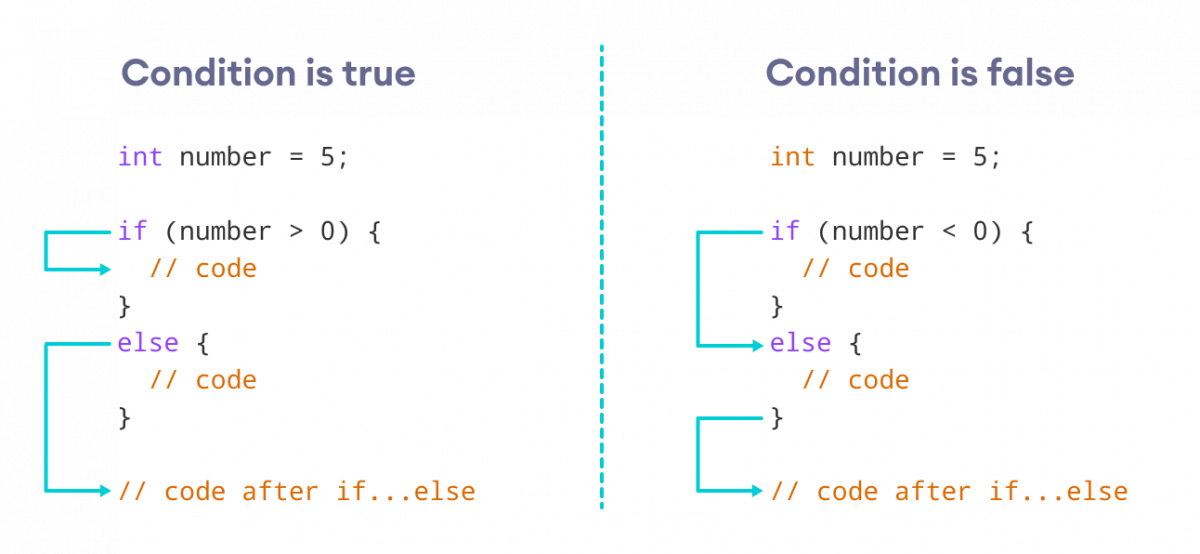
Example 3: Java if...else Statement
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int number = 10; // checks if number is greater than 0 if (number > 0) { System.out.println("The number is positive."); } // execute this block // if number is not greater than 0 else { System.out.println("The number is not positive."); } System.out.println("Statement outside if...else block"); } } Output
The number is positive. Statement outside if...else block
In the above example, we have a variable named number. Here, the test expression number > 0 checks if number is greater than 0.
Since the value of the number is 10, the test expression evaluates to true. Hence code inside the body of if is executed.
Now, change the value of the number to a negative integer. Let's say -5.
int number = -5; If we run the program with the new value of number, the output will be:
The number is not positive. Statement outside if...else block
Here, the value of number is -5. So the test expression evaluates to false. Hence code inside the body of else is executed.
3. Java if...else...if Statement
In Java, we have an if...else...if ladder, that can be used to execute one block of code among multiple other blocks.
if (condition1) { // codes } else if(condition2) { // codes } else if (condition3) { // codes } . . else { // codes } Here, if statements are executed from the top towards the bottom. When the test condition is true, codes inside the body of that if block is executed. And, program control jumps outside the if...else...if ladder.
If all test expressions are false, codes inside the body of else are executed.
How the if...else...if ladder works?
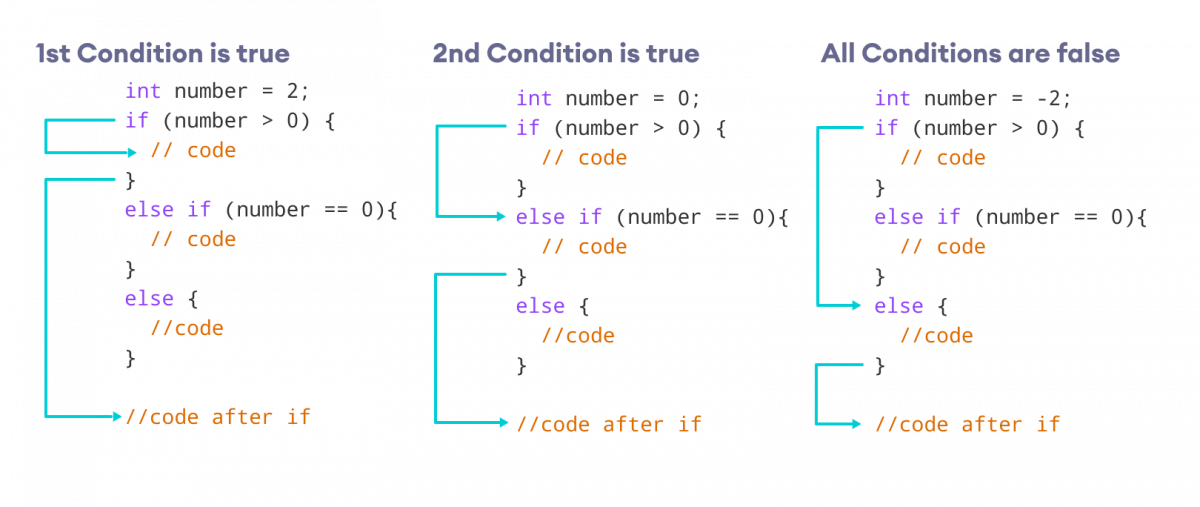
Example 4: Java if...else...if Statement
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int number = 0; // checks if number is greater than 0 if (number > 0) { System.out.println("The number is positive."); } // checks if number is less than 0 else if (number < 0) { System.out.println("The number is negative."); } // if both condition is false else { System.out.println("The number is 0."); } } } Output
The number is 0.
In the above example, we are checking whether number is positive, negative, or zero. Here, we have two condition expressions:
-
number > 0- checks if number is greater than 0 -
number < 0- checks if number is less than 0
Here, the value of number is 0. So both the conditions evaluate to false. Hence the statement inside the body of else is executed.
Note: Java provides a special operator called ternary operator, which is a kind of shorthand notation of if...else...if statement. To learn about the ternary operator, visit Java Ternary Operator.
4. Java Nested if..else Statement
In Java, it is also possible to use if..else statements inside an if...else statement. It's called the nested if...else statement.
Here's a program to find the largest of 3 numbers using the nested if...else statement.
Example 5: Nested if...else Statement
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // declaring double type variables Double n1 = -1.0, n2 = 4.5, n3 = -5.3, largest; // checks if n1 is greater than or equal to n2 if (n1 >= n2) { // if...else statement inside the if block // checks if n1 is greater than or equal to n3 if (n1 >= n3) { largest = n1; } else { largest = n3; } } else { // if..else statement inside else block // checks if n2 is greater than or equal to n3 if (n2 >= n3) { largest = n2; } else { largest = n3; } } System.out.println("Largest Number: " + largest); } } Output:
Largest Number: 4.5
In the above programs, we have assigned the value of variables ourselves to make this easier.
However, in real-world applications, these values may come from user input data, log files, form submission, etc.
Source: https://www.programiz.com/java-programming/if-else-statement
0 Response to "If Else Ladder in Java Example"
Post a Comment